Precision Forging – with its natural advantages:
1- Near -Net Shape forging
2- Little machining or no machining need
3- Extra high Strenth and controlled sound internal structural
Precision Forging – Process Difference
- Hot Precision Forging :Materials for hot precision forging have low deformation resistance and good plasticity, making it easy to form relatively complex workpieces. However, due to strong oxidation, the surface quality and dimensional accuracy of the workpieces are relatively low. The commonly used process method for hot precision forging is closed-die forging.
- Cold Precision Forging is a precision forging process carried out at room temperature. The cold precision forging process has the following characteristics: the shape and size of the workpiece are relatively easy to control, avoiding errors caused by high temperature; the workpiece has high strength and precision, and good surface quality. During the cold forging forming process, the workpiece has poor plasticity and high deformation resistance, which places high requirements on molds and equipment, and it is difficult to form parts with complex structures.
- WarmPrecision Forging is a precision forging process carried out at a suitable temperature below the recrystallization temperature. The warm precision forming technology not only breaks through the limitations of cold forging, such as high deformation resistance, inability to form parts with overly complex shapes, and the need for additional intermediate heat treatment and surface treatment steps, but also overcomes the problem of reduced surface quality and dimensional accuracy caused by strong oxidation in hot forging. It simultaneously possesses the advantages of both cold forging and hot forging while overcoming the shortcomings of the two.
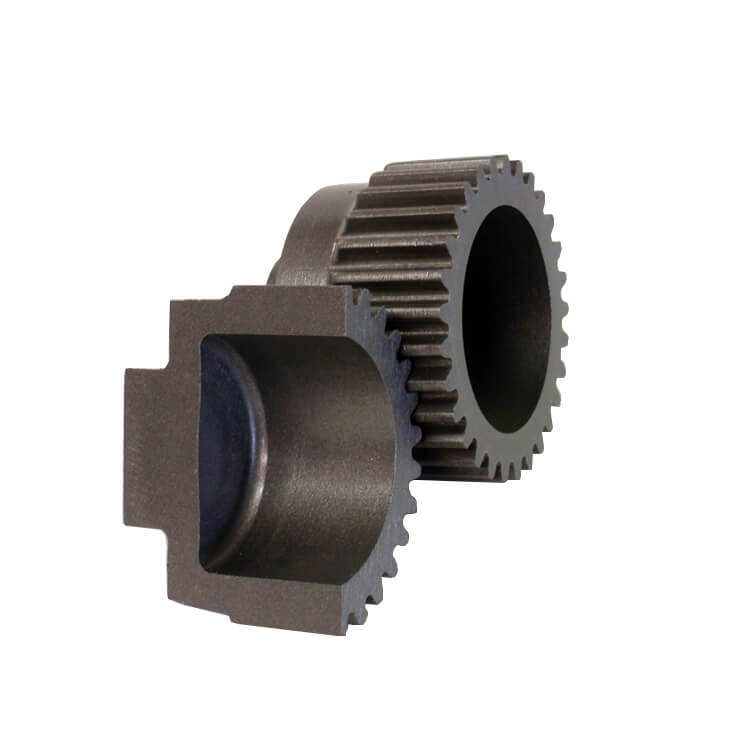
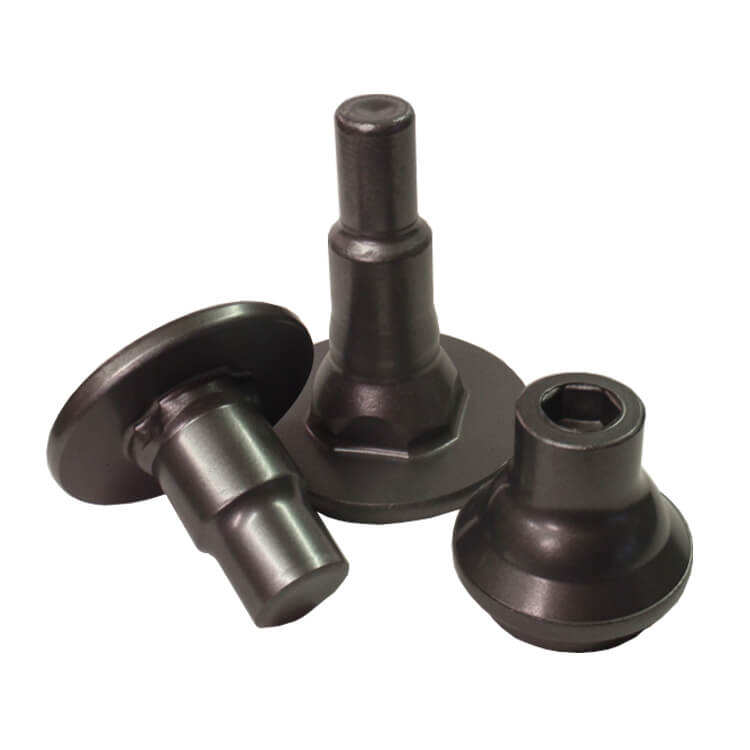
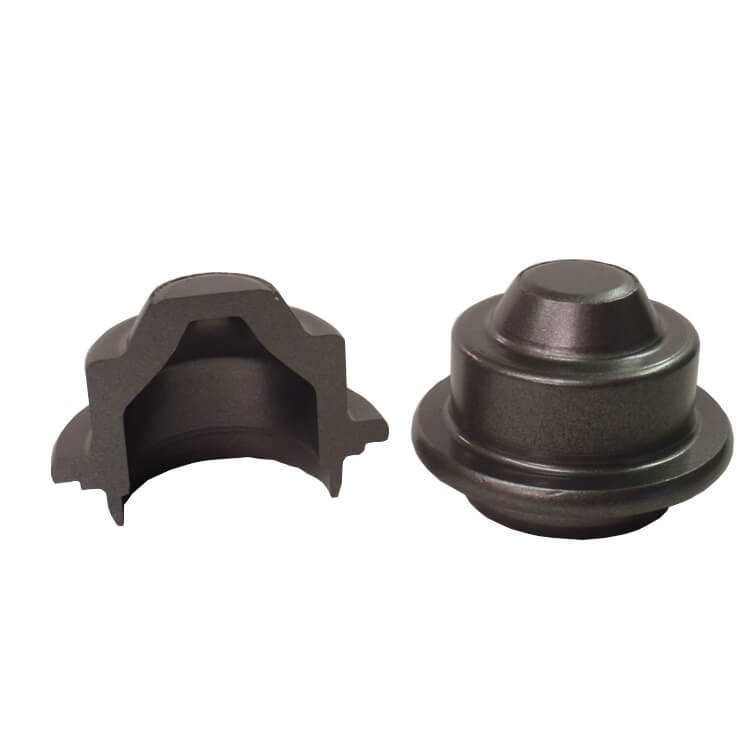



Leesh Foring Process
State-of-the-art manufacturing process ensuring highest quality standards

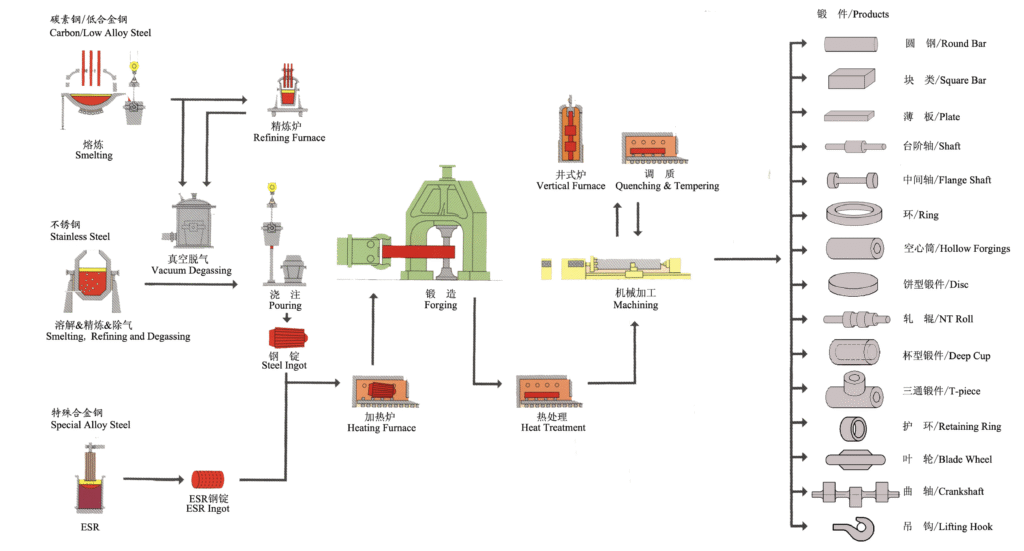
Hot Forging Materials We Use
High-quality steel materials for superior performance and durability
Carbon & Low Alloy Steel
Carbon Steel:
35, 45, CK22N, Q235
35, 45, CK22N, Q235
Mn Series:
16Mn, 20Mn2, 50Mn
16Mn, 20Mn2, 50Mn
Cr Series:
20Cr, 40Cr
20Cr, 40Cr
Structural Alloy Steel
Si-Mn:
20SiMn, 37SiMn2MoV
20SiMn, 37SiMn2MoV
Cr-Mo:
35CrMo, 42CrMo
35CrMo, 42CrMo
Cr-Ni-Mo:
34CrNiMo, 40CrNiMo
34CrNiMo, 40CrNiMo
Specialty Steels
Stainless Steel:
1Cr18Ni9Ti, 1Cr13
1Cr18Ni9Ti, 1Cr13
Super Alloy:
GH1, GH2, GH3, GH4 Series
GH1, GH2, GH3, GH4 Series
Refractory:
F91, F92, 15Cr2MoV
F91, F92, 15Cr2MoV
Pressure Vessel Steel
Standard:
09MnNiD, 16MnD
09MnNiD, 16MnD
Mo Alloy:
20MnMo, 15CrMo
20MnMo, 15CrMo
Certification:
ASME, GB Standards
ASME, GB Standards
Nuclear Power Steel
ASTM:
SA-182 Series
SA-182 Series
Pressure:
SA-266 Series
SA-266 Series
Grade:
Nuclear Quality
Nuclear Quality
Custom Materials
Composition:
Tailored to Requirements
Tailored to Requirements
Testing:
Full Material Analysis
Full Material Analysis
Documentation:
Complete Traceability
Complete Traceability
Applications of Hot Forging
Net shape forging is widely used in industries requiring high-strength, precision components with minimal production costs. Below are the key application areas and typical components:
Automotive
- Connecting rods
- Crankshafts
- Gear blanks
- Steering components
- Suspension parts
Aerospace
- Turbine blades
- Engine brackets
- Landing gear components
- Hydraulic fittings
- Structural forgings
Energy
- Wind turbine shafts
- Power generator components
- Oil & gas valves
- Pipeline fittings
- Nuclear reactor parts
Heavy Machinery
- Excavator bucket teeth
- Bulldozer linkages
- Crane hooks
- Transmission gears
- Hydraulic cylinder rods







