What is Close Die Forging?
Close die forging, a complex shape metal – forming process. In this process, a heated metal billet is placed between two dies. As the dies come together under immense pressure, the metal is forced to conform to the intricate shape of the die cavity. This results in parts with exceptional dimensional accuracy and a refined surface finish with less or no machining request.
The Process of Close Die Forging
The close die forging begins with die design. At Leesh our engineer team will desin the die as per customers’ drawing or model, after desgining, we will send to our machining shop for forging die maufacturing. Once the dies are ready, the metal billet is heated to its required forging temperature. This temperature varies depending on the type of metal, ensuring maximum malleability. The heated billet/raw material is then precisely positioned between the dies. A strong press then closes the dies, shaping the metal into the desired form. Post forging, the part will send to heat treatment to enhance its mechanical properties.
In most of the time, not only one die, it may 2 or 3 or more further dies to complete the finial shape.
Advantages of Close Die Forging
One of the primary benefits of close die forging is the high level of precision it offers. The process allows for the production of complex shapes with tight tolerances, reducing the need for extensive machining. Additionally, the forging process aligns the metal’s grain structure, resulting in parts that are stronger and more durable. This makes close die – forged components ideal for applications where reliability and performance are paramount, such as in the automotive, aerospace, and defense industries.
Leesh Close Die Forging Service
Leesh Die Forging Service already has decades of development, currently serves the auto, agriculture, earth moving, mining, and oil industries.
Based on the Leesh philosophy:
Integrity · Customer Focus · Commitment to Performance · Social Responsibility
Leesh has gained global reputation.
Based on the Leesh philosophy:
Integrity · Customer Focus · Commitment to Performance · Social Responsibility
Leesh has gained global reputation.
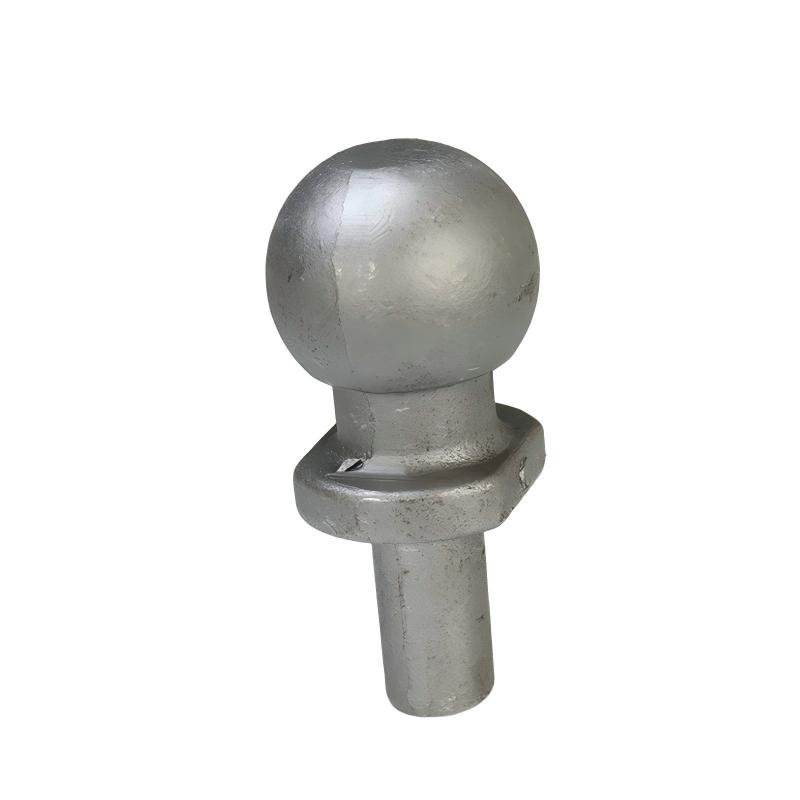
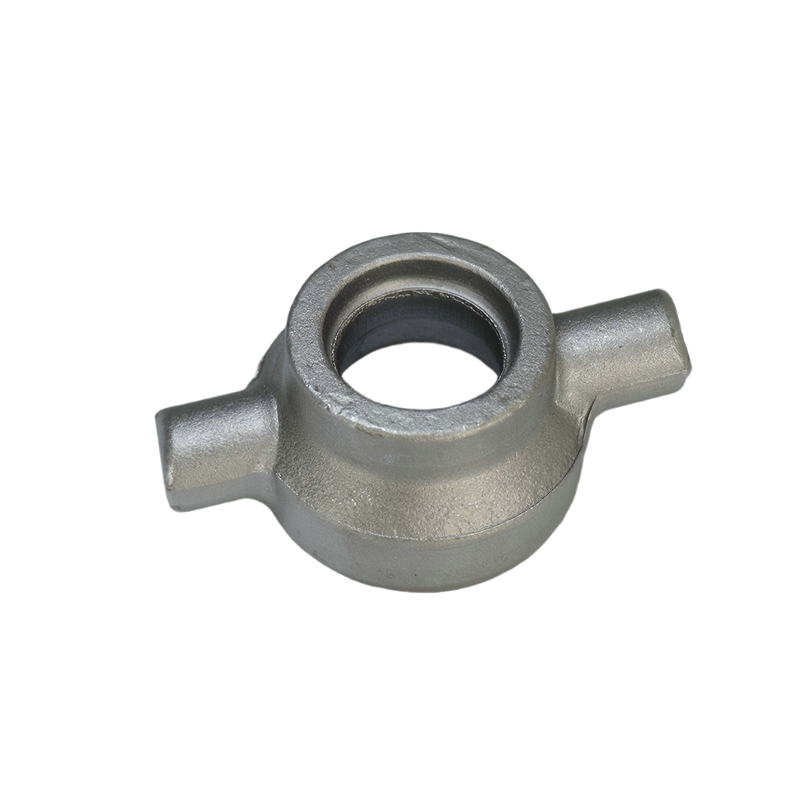
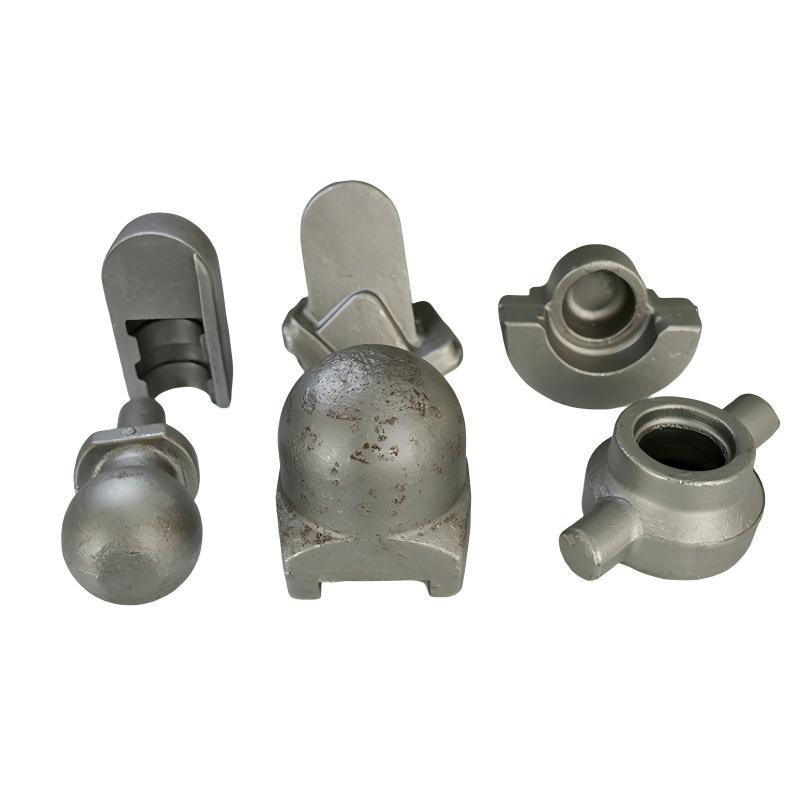



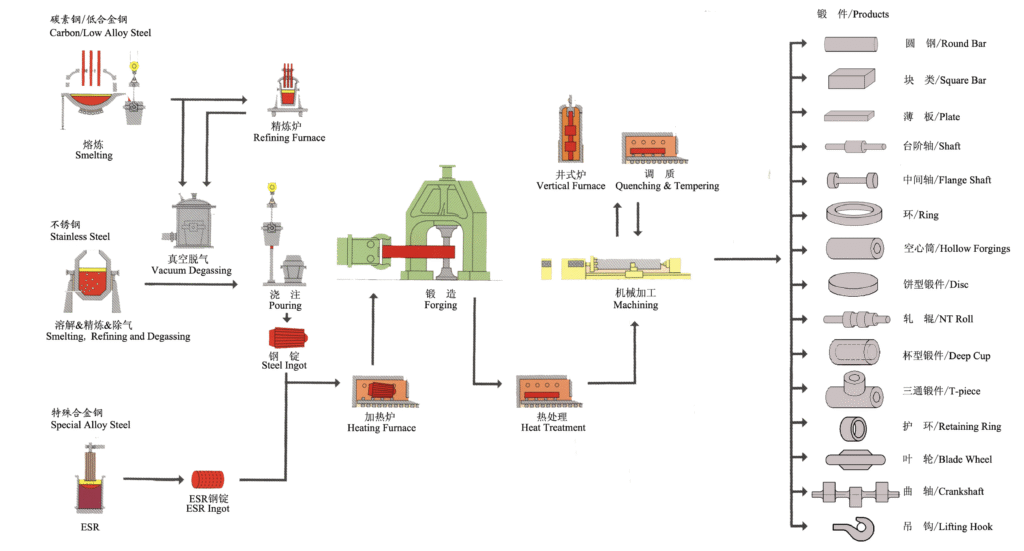
Leesh Foring Process
State-of-the-art manufacturing process ensuring highest quality standards

Hot Forging Materials We Use
High-quality steel materials for superior performance and durability
Carbon & Low Alloy Steel
Carbon Steel:
35, 45, CK22N, Q235
35, 45, CK22N, Q235
Mn Series:
16Mn, 20Mn2, 50Mn
16Mn, 20Mn2, 50Mn
Cr Series:
20Cr, 40Cr
20Cr, 40Cr
Structural Alloy Steel
Si-Mn:
20SiMn, 37SiMn2MoV
20SiMn, 37SiMn2MoV
Cr-Mo:
35CrMo, 42CrMo
35CrMo, 42CrMo
Cr-Ni-Mo:
34CrNiMo, 40CrNiMo
34CrNiMo, 40CrNiMo
Specialty Steels
Stainless Steel:
1Cr18Ni9Ti, 1Cr13
1Cr18Ni9Ti, 1Cr13
Super Alloy:
GH1, GH2, GH3, GH4 Series
GH1, GH2, GH3, GH4 Series
Refractory:
F91, F92, 15Cr2MoV
F91, F92, 15Cr2MoV
Pressure Vessel Steel
Standard:
09MnNiD, 16MnD
09MnNiD, 16MnD
Mo Alloy:
20MnMo, 15CrMo
20MnMo, 15CrMo
Certification:
ASME, GB Standards
ASME, GB Standards
Nuclear Power Steel
ASTM:
SA-182 Series
SA-182 Series
Pressure:
SA-266 Series
SA-266 Series
Grade:
Nuclear Quality
Nuclear Quality
Custom Materials
Composition:
Tailored to Requirements
Tailored to Requirements
Testing:
Full Material Analysis
Full Material Analysis
Documentation:
Complete Traceability
Complete Traceability
Applications of Hot Forging
Net shape forging is widely used in industries requiring high-strength, precision components with minimal production costs. Below are the key application areas and typical components:
Automotive
- Connecting rods
- Crankshafts
- Gear blanks
- Steering components
- Suspension parts
Aerospace
- Turbine blades
- Engine brackets
- Landing gear components
- Hydraulic fittings
- Structural forgings
Energy
- Wind turbine shafts
- Power generator components
- Oil & gas valves
- Pipeline fittings
- Nuclear reactor parts
Heavy Machinery
- Excavator bucket teeth
- Bulldozer linkages
- Crane hooks
- Transmission gears
- Hydraulic cylinder rods







