What is the Drop Forging Process?
Types of Drop Forging Processes
Hot Drop Forging Process
In the hot drop forging process, the metal workpiece is heated to a high temperature, typically above its recrystallization temperature. This makes the metal more malleable, allowing it to be easily shaped under the impact of the hammer or press. Hot drop forging is suitable for large – scale production and for working with metals like carbon steel and alloy steel. It can produce complex shapes with good grain flow, enhancing the mechanical properties of the final product.
Cold Drop Forging Process
The cold drop forging process, on the other hand, is carried out at room temperature. This process offers higher dimensional accuracy and a better surface finish compared to hot forging. However, it requires more force to deform the metal, as it is less malleable at lower temperatures. Cold drop forging is often used for small – to – medium – sized parts made of materials that can withstand the high forces involved, such as certain grades of carbon steel.
Net Shape Drop Forging Process
The net shape drop forging process aims to produce a forging that is close to the final shape of the component, minimizing the need for subsequent machining. This process requires precise control of the forging parameters and the use of advanced dies. It can significantly reduce production costs by saving material and machining time, especially for parts where high precision is required.
Materials for Drop Forging
Carbon Steel Drop Forging Process
Carbon steel is a commonly used material in drop forging. It offers a good balance of strength, ductility, and cost – effectiveness. The carbon content in the steel affects its properties, with higher carbon content resulting in increased hardness and strength but reduced ductility. Carbon steel drop forging is suitable for a wide range of applications, from simple tools to automotive components.
Alloy Steel Drop Forging Process
Alloy steel, which contains additional alloying elements such as chromium, nickel, and molybdenum, is used when enhanced properties are required. Alloy steel drop forging can produce components with higher strength, corrosion resistance, and heat resistance. These properties make alloy steel – forged parts ideal for applications in the aerospace, military, and high – performance automotive industries.



Leesh Foring Process
State-of-the-art manufacturing process ensuring highest quality standards

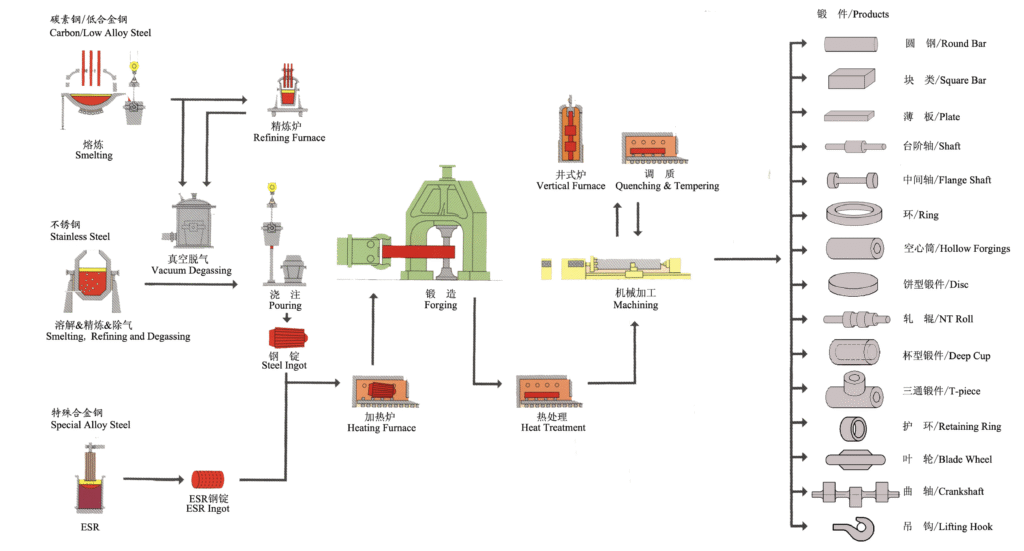
Hot Forging Materials We Use
High-quality steel materials for superior performance and durability
Carbon & Low Alloy Steel
35, 45, CK22N, Q235
16Mn, 20Mn2, 50Mn
20Cr, 40Cr
Structural Alloy Steel
20SiMn, 37SiMn2MoV
35CrMo, 42CrMo
34CrNiMo, 40CrNiMo
Specialty Steels
1Cr18Ni9Ti, 1Cr13
GH1, GH2, GH3, GH4 Series
F91, F92, 15Cr2MoV
Pressure Vessel Steel
09MnNiD, 16MnD
20MnMo, 15CrMo
ASME, GB Standards
Nuclear Power Steel
SA-182 Series
SA-266 Series
Nuclear Quality
Custom Materials
Tailored to Requirements
Full Material Analysis
Complete Traceability
Applications of Hot Forging
Net shape forging is widely used in industries requiring high-strength, precision components with minimal production costs. Below are the key application areas and typical components:
Automotive
- Connecting rods
- Crankshafts
- Gear blanks
- Steering components
- Suspension parts
Aerospace
- Turbine blades
- Engine brackets
- Landing gear components
- Hydraulic fittings
- Structural forgings
Energy
- Wind turbine shafts
- Power generator components
- Oil & gas valves
- Pipeline fittings
- Nuclear reactor parts
Heavy Machinery
- Excavator bucket teeth
- Bulldozer linkages
- Crane hooks
- Transmission gears
- Hydraulic cylinder rods







