Method of Manufacture
These alloys may be produced by any suitable melting practice. If any portion of the casting requires chilling or other special treatment, this shall be indicated on the inquiry and purchase order, accompanied by a drawing of the casting suitably marked.
Heat Treatment
- Castings shall be furnished in one of the following conditions:
- As-cast
- As-cast and stress relieved
- Hardened
- Hardened and stress relieved
- Annealed for machining
- Unless otherwise specified by the purchaser, the manufacturer shall supply the condition considered most suitable for the intended application.
- If the specified condition at time of delivery is not the final service condition, it is the purchaser’s responsibility to perform subsequent heat treatment.
- Class II and III alloys are often ordered annealed to a maximum hardness of 400 HB for machining. After machining, castings may be hardened. If annealing and machining are to be performed by the manufacturer as specified in the inquiry, contract, or order, the purchaser may specify delivery in the hardened condition. If the purchaser specifies delivery in the annealed condition, subsequent hardening (and stress relieving, if required) is the purchaser’s responsibility.
Hardness Requirements
- Castings shall conform to the hardness requirements specified in Table 2.
- Hardness tests shall be made on the original casting surface or not more than 1⁄8 in. [3 mm] below that surface.
Hardness Test Method
- Hardness testing shall be performed by one of the following methods as specified by the purchaser:
- Test Method E10 (Brinell), using a tungsten carbide ball indenter and a 3000 kgf load.
- Test Method E18 (Rockwell), using a diamond cone indenter, 150 kgf load, and Rockwell C scale.
- Test Method E92 (Vickers).
Table 1 – Chemical Requirements (Weight %)
| Class | Type | Grade | C | Mn | Si | Ni | Cr | Mo | Cu | P | S |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | A | Ni-Cr-HiC | 2.8–3.6 | ≤2.0 | ≤0.8 | 3.3–5.0 | 1.4–4.0 | ≤1.0 | … | ≤0.3 | ≤0.15 |
| I | B | Ni-Cr-LoC | 2.4–3.0 | ≤2.0 | ≤0.8 | 3.3–5.0 | 1.4–4.0 | ≤1.0 | … | ≤0.3 | ≤0.15 |
| I | C | Ni-Cr-GB | 2.5–3.7 | ≤2.0 | ≤0.8 | ≤4.0 | 1.0–2.5 | ≤1.0 | … | ≤0.3 | ≤0.15 |
| I | D | Ni-HiCr | 2.5–3.6 | ≤2.0 | ≤2.0 | 4.5–7.0 | 7.0–11.0 | ≤1.5 | … | ≤0.10 | ≤0.15 |
| II | A | 12% Cr | 2.0–3.3 | ≤2.0 | ≤1.5 | ≤2.5 | 11.0–14.0 | ≤3.0 | ≤1.2 | ≤0.10 | ≤0.06 |
| II | B | 15% Cr-Mo | 2.0–3.3 | ≤2.0 | ≤1.5 | ≤2.5 | 14.0–18.0 | ≤3.0 | ≤1.2 | ≤0.10 | ≤0.06 |
| II | D | 20% Cr-Mo | 2.0–3.3 | ≤2.0 | 1.0–2.2 | ≤2.5 | 18.0–23.0 | ≤3.0 | ≤1.2 | ≤0.10 | ≤0.06 |
| III | A | 25% Cr | 2.0–3.3 | ≤2.0 | ≤1.5 | ≤2.5 | 23.0–30.0 | ≤3.0 | ≤1.2 | ≤0.10 | ≤0.06 |
Table 2 – Hardness Requirements
| Class | Type | Grade | As-Cast or As-Cast + Stress Relieved (min) | Hardened or Hardened + Stress Relieved | Chilled As-Cast (min) | Annealed (max) | Typical Values | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HRC | HV | HB | HRC | HV | HB | HRC | HV | HB | HRC | HV | HB | HRC | HV | HB | |||
| I | A | Ni-Cr-HiC | 550 | 53 | 600 | 600 | 56 | 660 | 650 | 59 | 715 | 600 | 56 | 660 | … | … | … |
| II | A | 12% Cr | 550 | 53 | 600 | 600 | 56 | 660 | 650 | 59 | 715 | 550 | 53 | 600 | 400 | 41 | 430 |
| II | B | 15% Cr-Mo | 450 | 46 | 485 | 600 | 56 | 660 | 650 | 59 | 715 | … | … | … | 400 | 41 | 430 |
| III | A | 25% Cr | 450 | 46 | 485 | 600 | 56 | 660 | 650 | 59 | 715 | … | … | … | 400 | 41 | 430 |
Additional Notes:
- 90% of the minimum surface hardness shall be maintained to a depth of 40% of the casting section thickness; any softer material shall be confined to the thermal center of the casting.
- Sampling procedures shall be mutually agreed upon by the supplier and purchaser.
- Non-chilled areas of castings shall meet the minimum hardness requirements or sand-casting conditions.
Abrasion Resistant White Iron Castings ASTM A532 / A532M – Equivalent Grades in China and Other Countries
1. Overview of ASTM A532 / A532M Standard
ASTM A532 / A532M is a standard specification developed by the American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM) for abrasion resistant white iron castings, with the latest version being A532/A532M-10(2023). This standard covers a series of alloyed white irons designed for high abrasion resistance in applications such as mining, ore grinding, earthmoving and manufacturing industries. It explicitly excludes simple low-alloy white irons consisting only of iron carbides and pearlite.
1.1 Classification and Types
ASTM A532 classifies abrasion resistant white iron castings into four classes (Class I-IV) and multiple types (Type A-D), mainly based on alloy element content and microstructural differences:
| Class | Main Alloy System | Typical Types | Application Characteristics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Class I | Ni-Cr Alloy (Ni-Hard Iron) | A, B, C, D | High hardness, medium toughness, suitable for medium impact and abrasion environments |
| Class II | Cr-Mo Alloy (12-20% Cr) | A(12% Cr), B(15% Cr-Mo), D(20% Cr-Mo) | Balanced wear resistance and toughness, widely used in mining and building materials industries |
| Class III | High Cr Alloy (25-30% Cr) | A(25% Cr), B(28% Cr), C(30% Cr) | Extremely high wear resistance, optimal for low-impact and high-abrasion environments (e.g., ball mill liners) |
| Class IV | Special Alloy System | Various Types | Customized for specific working conditions (e.g., high-temperature abrasion environments) |
1.2 Key Technical Requirements
- Chemical Composition: Carbon content is usually 2.0-3.6%, chromium content ranges from 11% to 30%, with strict regulations according to classes and types
- Hardness Requirement: Divided into multiple grades based on heat treatment status, usually 450-650 HB (46-60 HRC); high-chromium grades can reach over 620 HB
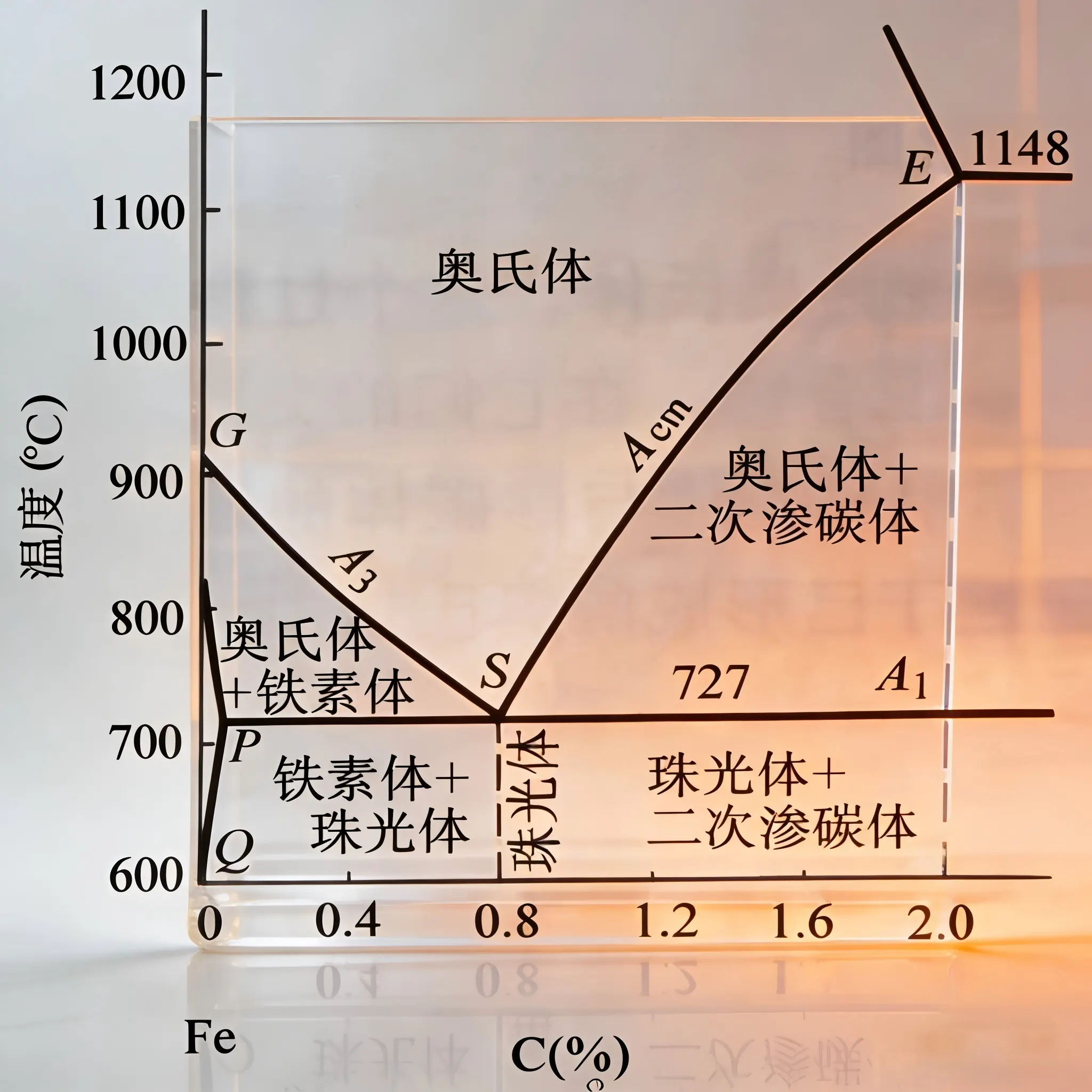
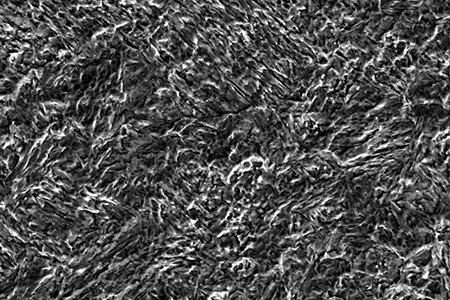
- Microstructure: Must contain carbides (e.g., M₇C₃ chromium carbide), and the matrix is usually martensite or austenite-martensite mixed structure
2. Equivalent Chinese Standard and Grades
The corresponding national standard in China is GB/T 8263-2010《Abrasion Resistant White Iron Castings》, which is a modified adoption (MOD) of ASTM A532/A532M-93a(2008).
2.1 Chinese Grade System
GB/T 8263-2010 uses BTMCr (Bainitic/Martensitic Abrasion Resistant White Iron – Chromium Series) and BTMNiCr (Bainitic/Martensitic Abrasion Resistant White Iron – Nickel-Chromium Series) as grade prefixes, corresponding to different classes and types of ASTM A532.
2.2 Main Corresponding Relationships
| ASTM A532 Class & Type | GB/T 8263-2010 Grade | Main Composition | Hardness Requirement |
|---|---|---|---|
| Class I Type A (Ni-Hard 1) | BTMNiCr4 | 4% Ni, 1.5% Cr | ≥55 HRC |
| Class I Type B (Ni-Hard 2) | BTMNiCr8 | 8% Ni, 4% Cr | ≥58 HRC |
| Class I Type D (Ni-Hard 4) | BTMNiCr3 | 3% Ni, 3% Cr | ≥55 HRC |
| Class II Type A (12% Cr) | BTMCr12 | 12% Cr | ≥56 HRC |
| Class II Type B (15% Cr-Mo) | BTMCr15Mo | 15% Cr, 1% Mo | ≥56 HRC |
| Class II Type D (20% Cr-Mo) | BTMCr20Mo | 20% Cr, 1.5% Mo | ≥56 HRC |
| Class III Type A (25% Cr) | BTMCr26 | 26% Cr | ≥60 HRC |
2.3 Explanation of Standard Differences
Compared with ASTM A532, GB/T 8263-2010 has the following main differences:
- Added three grades (BTMCr2, BTMCr8 and BTMCr12-DT) to adapt to China’s production practice
- Adopted different grade designation methods (BTMCr series vs ASTM Class-Type system)
- Added requirements for casting surface quality, sampling and inspection rules, as well as marking, storage, packaging and transportation
- Raised the surface hardness requirement for some high-chromium grades, and added the hardness requirement at 40% of the casting section depth
3. Equivalent Standards and Grades in Other Countries/Regions
3.1 European Standard (EN)
The corresponding European standard is EN 12513《Abrasion Resistant Cast Irons》, identical or equivalent to ASTM A532, with the main grades as follows:
| ASTM A532 Class & Type | EN 12513 Grade | European Standard Code |
|---|---|---|
| Class II Type A (12% Cr) | EN-GJN-HB555(XCr11) | EN 5.5607 |
| Class II Type B (15% Cr-Mo) | EN-GJN-HB555(XCr14) | EN 5.5608 |
| Class II Type D (20% Cr-Mo) | EN-GJN-HB555(XCr18) | EN 5.5609 |
| Class III Type A (25% Cr) | EN-GJN-HB555(XCr23) | EN 5.5610 |
| Class I Type A (Ni-Hard 1) | EN-GJN-HB555(NiCr5) | EN 5.5601 |
3.2 German Standard (DIN)
The German standard is DIN 1695《Abrasion Resistant White Iron Castings》, with the corresponding grades compared to ASTM A532 as follows:
| ASTM A532 Class & Type | DIN 1695 Grade | German Standard Code |
|---|---|---|
| Class II Type B (15% Cr-Mo) | G-X 300 CrMo 15 3 | DIN 0.9635 |
| Class II Type B (15% Cr-Mo-Ni) | G-X 300 CrMoNi 15 2 1 | DIN 0.9640 |
| Class III Type A (25% Cr) | G-X 280 Cr 26 | DIN 0.9650 |
| Class I Type A (Ni-Hard 1) | G-X 250 NiCr 5 1 | DIN 0.9601 |
3.3 Japanese Standard (JIS)
The corresponding Japanese standard is JIS G5131《Abrasion Resistant Cast Irons》, equivalent to ASTM A532, with the main grades including:
- Ni-Hard Series: Corresponding to various types of ASTM Class I (e.g., Ni-Hard 1, 2, 4)
- High Chromium Iron Series: Corresponding to ASTM Class II and III (e.g., HC12, HC15, HC20, HC25 with chromium content of 12%, 15%, 20% and 25% respectively)
3.4 Other Countries/Regions Standards
| Country/Region | Standard No. | Equivalence | Characteristics |
|---|---|---|---|
| UK (BS) | BS 4844 | Equivalent to ASTM A532 | Adopts a similar classification system with a complete range of Ni-Hard and high chromium series |
| Australia (AS) | AS 2027 | Equivalent to ASTM A532 | Combines the characteristics of EN and ASTM, adapted to the needs of Australia’s mining industry |
| Russia (GOST) | GOST 7769 | Equivalent to ASTM A532 | Ni-Hard iron grades are CHN series, and high chromium grades are X series |
4. Explanation of Standard Equivalence
- Equivalence Level: China’s GB/T 8263-2010 is a modified adoption (MOD) of ASTM A532/A532M-93a(2008); European EN 12513 and German DIN 1695 are identical adoption (IDT) or equivalent adoption (EQV)
- Technical Differences: National standards have slight differences in grade designation, partial element content ranges and inspection requirements, but the core performance (wear resistance, hardness, microstructure) remains consistent
- Application Interchangeability: Abrasion resistant white iron castings complying with national equivalent standards can be used interchangeably in most industrial applications, but attention should be paid to the precise matching of heat treatment status and hardness grade
5. Typical Application Fields
ASTM A532 and its equivalent grade abrasion resistant white iron castings are widely used in the following industries:
- Mining Equipment: Crusher jaw plates, cone crusher liners, ball mill liners, grinding media
- Material Handling: Conveyor blades, chutes, hoppers, vibrating screen plates
- Construction Machinery: Excavator bucket teeth, loader buckets, bulldozer blades
- Energy and Power: Coal mill rollers, grinding discs, exhaust fan impellers
- Building Materials Industry: Cement mill liners, concrete mixing blades, sand making machine hammers
Abrasion Resistant White Iron Castings ASTM A532 / A532M

Method of Manufacture
These alloys may be produced by any suitable melting practice. If any portion of the casting requires chilling or other special treatment, this shall be indicated on the inquiry and purchase order, accompanied by a drawing of the casting suitably marked.
Heat Treatment
- Castings shall be furnished in one of the following conditions:
- As-cast
- As-cast and stress relieved
- Hardened
- Hardened and stress relieved
- Annealed for machining
- Unless otherwise specified by the purchaser, the manufacturer shall supply the condition considered most suitable for the intended application.
- If the specified condition at time of delivery is not the final service condition, it is the purchaser’s responsibility to perform subsequent heat treatment.
- Class II and III alloys are often ordered annealed to a maximum hardness of 400 HB for machining. After machining, castings may be hardened. If annealing and machining are to be performed by the manufacturer as specified in the inquiry, contract, or order, the purchaser may specify delivery in the hardened condition. If the purchaser specifies delivery in the annealed condition, subsequent hardening (and stress relieving, if required) is the purchaser’s responsibility.
Hardness Requirements
- Castings shall conform to the hardness requirements specified in Table 2.
- Hardness tests shall be made on the original casting surface or not more than 1⁄8 in. [3 mm] below that surface.
Hardness Test Method
- Hardness testing shall be performed by one of the following methods as specified by the purchaser:
- Test Method E10 (Brinell), using a tungsten carbide ball indenter and a 3000 kgf load.
- Test Method E18 (Rockwell), using a diamond cone indenter, 150 kgf load, and Rockwell C scale.
- Test Method E92 (Vickers).
Table 1 – Chemical Requirements (Weight %)
| Class | Type | Grade | C | Mn | Si | Ni | Cr | Mo | Cu | P | S |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | A | Ni-Cr-HiC | 2.8–3.6 | ≤2.0 | ≤0.8 | 3.3–5.0 | 1.4–4.0 | ≤1.0 | … | ≤0.3 | ≤0.15 |
| I | B | Ni-Cr-LoC | 2.4–3.0 | ≤2.0 | ≤0.8 | 3.3–5.0 | 1.4–4.0 | ≤1.0 | … | ≤0.3 | ≤0.15 |
| I | C | Ni-Cr-GB | 2.5–3.7 | ≤2.0 | ≤0.8 | ≤4.0 | 1.0–2.5 | ≤1.0 | … | ≤0.3 | ≤0.15 |
| I | D | Ni-HiCr | 2.5–3.6 | ≤2.0 | ≤2.0 | 4.5–7.0 | 7.0–11.0 | ≤1.5 | … | ≤0.10 | ≤0.15 |
| II | A | 12% Cr | 2.0–3.3 | ≤2.0 | ≤1.5 | ≤2.5 | 11.0–14.0 | ≤3.0 | ≤1.2 | ≤0.10 | ≤0.06 |
| II | B | 15% Cr-Mo | 2.0–3.3 | ≤2.0 | ≤1.5 | ≤2.5 | 14.0–18.0 | ≤3.0 | ≤1.2 | ≤0.10 | ≤0.06 |
| II | D | 20% Cr-Mo | 2.0–3.3 | ≤2.0 | 1.0–2.2 | ≤2.5 | 18.0–23.0 | ≤3.0 | ≤1.2 | ≤0.10 | ≤0.06 |
| III | A | 25% Cr | 2.0–3.3 | ≤2.0 | ≤1.5 | ≤2.5 | 23.0–30.0 | ≤3.0 | ≤1.2 | ≤0.10 | ≤0.06 |
Table 2 – Hardness Requirements
| Class | Type | Grade | As-Cast or As-Cast + Stress Relieved (min) | Hardened or Hardened + Stress Relieved | Chilled As-Cast (min) | Annealed (max) | Typical Values | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HRC | HV | HB | HRC | HV | HB | HRC | HV | HB | HRC | HV | HB | HRC | HV | HB | |||
| I | A | Ni-Cr-HiC | 550 | 53 | 600 | 600 | 56 | 660 | 650 | 59 | 715 | 600 | 56 | 660 | … | … | … |
| II | A | 12% Cr | 550 | 53 | 600 | 600 | 56 | 660 | 650 | 59 | 715 | 550 | 53 | 600 | 400 | 41 | 430 |
| II | B | 15% Cr-Mo | 450 | 46 | 485 | 600 | 56 | 660 | 650 | 59 | 715 | … | … | … | 400 | 41 | 430 |
| III | A | 25% Cr | 450 | 46 | 485 | 600 | 56 | 660 | 650 | 59 | 715 | … | … | … | 400 | 41 | 430 |
Additional Notes:
- 90% of the minimum surface hardness shall be maintained to a depth of 40% of the casting section thickness; any softer material shall be confined to the thermal center of the casting.
- Sampling procedures shall be mutually agreed upon by the supplier and purchaser.
- Non-chilled areas of castings shall meet the minimum hardness requirements or sand-casting conditions.
Abrasion Resistant White Iron Castings ASTM A532 / A532M – Equivalent Grades in China and Other Countries
1. Overview of ASTM A532 / A532M Standard
ASTM A532 / A532M is a standard specification developed by the American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM) for abrasion resistant white iron castings, with the latest version being A532/A532M-10(2023). This standard covers a series of alloyed white irons designed for high abrasion resistance in applications such as mining, ore grinding, earthmoving and manufacturing industries. It explicitly excludes simple low-alloy white irons consisting only of iron carbides and pearlite.
1.1 Classification and Types
ASTM A532 classifies abrasion resistant white iron castings into four classes (Class I-IV) and multiple types (Type A-D), mainly based on alloy element content and microstructural differences:
| Class | Main Alloy System | Typical Types | Application Characteristics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Class I | Ni-Cr Alloy (Ni-Hard Iron) | A, B, C, D | High hardness, medium toughness, suitable for medium impact and abrasion environments |
| Class II | Cr-Mo Alloy (12-20% Cr) | A(12% Cr), B(15% Cr-Mo), D(20% Cr-Mo) | Balanced wear resistance and toughness, widely used in mining and building materials industries |
| Class III | High Cr Alloy (25-30% Cr) | A(25% Cr), B(28% Cr), C(30% Cr) | Extremely high wear resistance, optimal for low-impact and high-abrasion environments (e.g., ball mill liners) |
| Class IV | Special Alloy System | Various Types | Customized for specific working conditions (e.g., high-temperature abrasion environments) |
1.2 Key Technical Requirements
- Chemical Composition: Carbon content is usually 2.0-3.6%, chromium content ranges from 11% to 30%, with strict regulations according to classes and types
- Hardness Requirement: Divided into multiple grades based on heat treatment status, usually 450-650 HB (46-60 HRC); high-chromium grades can reach over 620 HB
- Microstructure: Must contain carbides (e.g., M₇C₃ chromium carbide), and the matrix is usually martensite or austenite-martensite mixed structure
2. Equivalent Chinese Standard and Grades
The corresponding national standard in China is GB/T 8263-2010《Abrasion Resistant White Iron Castings》, which is a modified adoption (MOD) of ASTM A532/A532M-93a(2008).
2.1 Chinese Grade System
GB/T 8263-2010 uses BTMCr (Bainitic/Martensitic Abrasion Resistant White Iron – Chromium Series) and BTMNiCr (Bainitic/Martensitic Abrasion Resistant White Iron – Nickel-Chromium Series) as grade prefixes, corresponding to different classes and types of ASTM A532.
2.2 Main Corresponding Relationships
| ASTM A532 Class & Type | GB/T 8263-2010 Grade | Main Composition | Hardness Requirement |
|---|---|---|---|
| Class I Type A (Ni-Hard 1) | BTMNiCr4 | 4% Ni, 1.5% Cr | ≥55 HRC |
| Class I Type B (Ni-Hard 2) | BTMNiCr8 | 8% Ni, 4% Cr | ≥58 HRC |
| Class I Type D (Ni-Hard 4) | BTMNiCr3 | 3% Ni, 3% Cr | ≥55 HRC |
| Class II Type A (12% Cr) | BTMCr12 | 12% Cr | ≥56 HRC |
| Class II Type B (15% Cr-Mo) | BTMCr15Mo | 15% Cr, 1% Mo | ≥56 HRC |
| Class II Type D (20% Cr-Mo) | BTMCr20Mo | 20% Cr, 1.5% Mo | ≥56 HRC |
| Class III Type A (25% Cr) | BTMCr26 | 26% Cr | ≥60 HRC |
2.3 Explanation of Standard Differences
Compared with ASTM A532, GB/T 8263-2010 has the following main differences:
- Added three grades (BTMCr2, BTMCr8 and BTMCr12-DT) to adapt to China’s production practice
- Adopted different grade designation methods (BTMCr series vs ASTM Class-Type system)
- Added requirements for casting surface quality, sampling and inspection rules, as well as marking, storage, packaging and transportation
- Raised the surface hardness requirement for some high-chromium grades, and added the hardness requirement at 40% of the casting section depth
3. Equivalent Standards and Grades in Other Countries/Regions
3.1 European Standard (EN)
The corresponding European standard is EN 12513《Abrasion Resistant Cast Irons》, identical or equivalent to ASTM A532, with the main grades as follows:
| ASTM A532 Class & Type | EN 12513 Grade | European Standard Code |
|---|---|---|
| Class II Type A (12% Cr) | EN-GJN-HB555(XCr11) | EN 5.5607 |
| Class II Type B (15% Cr-Mo) | EN-GJN-HB555(XCr14) | EN 5.5608 |
| Class II Type D (20% Cr-Mo) | EN-GJN-HB555(XCr18) | EN 5.5609 |
| Class III Type A (25% Cr) | EN-GJN-HB555(XCr23) | EN 5.5610 |
| Class I Type A (Ni-Hard 1) | EN-GJN-HB555(NiCr5) | EN 5.5601 |
3.2 German Standard (DIN)
The German standard is DIN 1695《Abrasion Resistant White Iron Castings》, with the corresponding grades compared to ASTM A532 as follows:
| ASTM A532 Class & Type | DIN 1695 Grade | German Standard Code |
|---|---|---|
| Class II Type B (15% Cr-Mo) | G-X 300 CrMo 15 3 | DIN 0.9635 |
| Class II Type B (15% Cr-Mo-Ni) | G-X 300 CrMoNi 15 2 1 | DIN 0.9640 |
| Class III Type A (25% Cr) | G-X 280 Cr 26 | DIN 0.9650 |
| Class I Type A (Ni-Hard 1) | G-X 250 NiCr 5 1 | DIN 0.9601 |
3.3 Japanese Standard (JIS)
The corresponding Japanese standard is JIS G5131《Abrasion Resistant Cast Irons》, equivalent to ASTM A532, with the main grades including:
- Ni-Hard Series: Corresponding to various types of ASTM Class I (e.g., Ni-Hard 1, 2, 4)
- High Chromium Iron Series: Corresponding to ASTM Class II and III (e.g., HC12, HC15, HC20, HC25 with chromium content of 12%, 15%, 20% and 25% respectively)
3.4 Other Countries/Regions Standards
| Country/Region | Standard No. | Equivalence | Characteristics |
|---|---|---|---|
| UK (BS) | BS 4844 | Equivalent to ASTM A532 | Adopts a similar classification system with a complete range of Ni-Hard and high chromium series |
| Australia (AS) | AS 2027 | Equivalent to ASTM A532 | Combines the characteristics of EN and ASTM, adapted to the needs of Australia’s mining industry |
| Russia (GOST) | GOST 7769 | Equivalent to ASTM A532 | Ni-Hard iron grades are CHN series, and high chromium grades are X series |
4. Explanation of Standard Equivalence
- Equivalence Level: China’s GB/T 8263-2010 is a modified adoption (MOD) of ASTM A532/A532M-93a(2008); European EN 12513 and German DIN 1695 are identical adoption (IDT) or equivalent adoption (EQV)
- Technical Differences: National standards have slight differences in grade designation, partial element content ranges and inspection requirements, but the core performance (wear resistance, hardness, microstructure) remains consistent
- Application Interchangeability: Abrasion resistant white iron castings complying with national equivalent standards can be used interchangeably in most industrial applications, but attention should be paid to the precise matching of heat treatment status and hardness grade
5. Typical Application Fields
ASTM A532 and its equivalent grade abrasion resistant white iron castings are widely used in the following industries:
- Mining Equipment: Crusher jaw plates, cone crusher liners, ball mill liners, grinding media
- Material Handling: Conveyor blades, chutes, hoppers, vibrating screen plates
- Construction Machinery: Excavator bucket teeth, loader buckets, bulldozer blades
- Energy and Power: Coal mill rollers, grinding discs, exhaust fan impellers
- Building Materials Industry: Cement mill liners, concrete mixing blades, sand making machine hammers