ZG06Cr13Ni5Mo High Strength Martensitic Stainless Steel Castings
Chinese Standard: ZG06Cr13Ni5Mo, 04Cr13Ni5Mo (New Grade), 0Cr13Ni5Mo (Old Grade), S41595 (Digital Grade)
American Standard: ASTM S41500, UNS F6NM
Japanese Standard: JIS SUS F6NM, JIS SCS6
German Standard: DIN 1.4313
European Standard: EN X3CrNiMo13-4
Abstract
ZG06Cr13Ni5Mo is a super low carbon martensitic stainless steel casting material with excellent comprehensive properties. Through precise composition design and advanced heat treatment processes, it achieves the perfect combination of high strength and good corrosion resistance. This report systematically elaborates on the chemical composition, microstructural characteristics, mechanical properties, heat treatment processes, casting technology, and engineering applications of ZG06Cr13Ni5Mo.
Research shows that while maintaining a tensile strength of 1050-1250MPa, this material retains an uniform elongation of over 12% and excellent corrosion resistance, with a pitting potential reaching +320mV(SCE) in 3.5% NaCl solution. Through the dual refining process of vacuum induction melting and argon oxygen decarburization, the material purity is significantly improved, with sulfur and phosphorus impurity contents controlled below 50ppm.
In engineering applications, ZG06Cr13Ni5Mo has been successfully applied to key components such as hydro turbine runners, offshore platform anchor chain systems, and nuclear power equipment, demonstrating broad application prospects and technical advantages. This report aims to provide comprehensive technical references for relevant engineering design, material selection, and process optimization.
Keywords: ZG06Cr13Ni5Mo; Martensitic Stainless Steel; Casting Material; Mechanical Properties; Corrosion Resistance; Engineering Applications
1. Introduction
1.1 Material Overview
As a new generation of high-strength martensitic stainless steel casting material, ZG06Cr13Ni5Mo is a high-performance alloy developed from traditional 13Cr martensitic stainless steel. By reducing the carbon content (≤0.06%) and optimizing the ratio of alloying elements such as nickel and molybdenum, this material successfully solves the technical challenge of balancing strength, toughness, and corrosion resistance in traditional martensitic stainless steels. Its research and development breakthrough marks important progress in China’s high-end stainless steel material field, providing key material support for major equipment manufacturing.
1.2 Development Background and Significance
As equipment in energy, marine, nuclear power and other fields develops towards larger scale and higher parameters, performance requirements for structural materials become increasingly stringent. The limitations of traditional stainless steel materials in strength, toughness, corrosion resistance and other aspects are gradually emerging, failing to meet the requirements of extreme working conditions. The successful development of ZG06Cr13Ni5Mo fills the gap in domestic high-strength corrosion-resistant stainless steel casting materials, and is of great strategic significance for improving the independent level of China’s major equipment and ensuring national energy security.
1.3 Research Objectives and Content
This report aims to comprehensively and systematically introduce the technical characteristics of ZG06Cr13Ni5Mo material, including chemical composition design, microstructural characteristics, mechanical properties, heat treatment processes, casting technology, and engineering application cases. Through in-depth analysis of the material’s technical advantages and application prospects, it provides scientific basis and technical guidance for engineering design, material selection, and process optimization in relevant fields.
2. Material Basic Characteristics
2.1 Chemical Composition Design
The chemical composition design of ZG06Cr13Ni5Mo embodies modern alloy design concepts, achieving performance optimization through precise control of element contents.
| Element | Content Range (%) | Function and Significance |
|---|---|---|
| C | ≤0.06 | Reduce carbon content to improve weldability and toughness; controlling below 0.06% can effectively avoid welding cracks |
| Cr | 11.5~13.5 | Forms dense chromium oxide passivation film, providing basic corrosion resistance; content around 13% ensures good oxidation resistance |
| Ni | 4.5~6.0 | Improves toughness and plasticity, stabilizes austenite structure; content around 5% significantly enhances low-temperature impact performance |
| Mo | 0.40~1.00 | Improves pitting and crevice corrosion resistance, refines grains, enhances high-temperature strength |
| Si | ≤1.00 | Deoxidizer, improves casting performance; controlled at low level to avoid reducing toughness |
| Mn | ≤1.00 | Improves hardenability, enhances hot working performance |
| P | ≤0.035 | Impurity element; strictly controlled to avoid reducing toughness and corrosion resistance |
| S | ≤0.030 | Impurity element; strictly controlled to avoid reducing toughness and corrosion resistance |
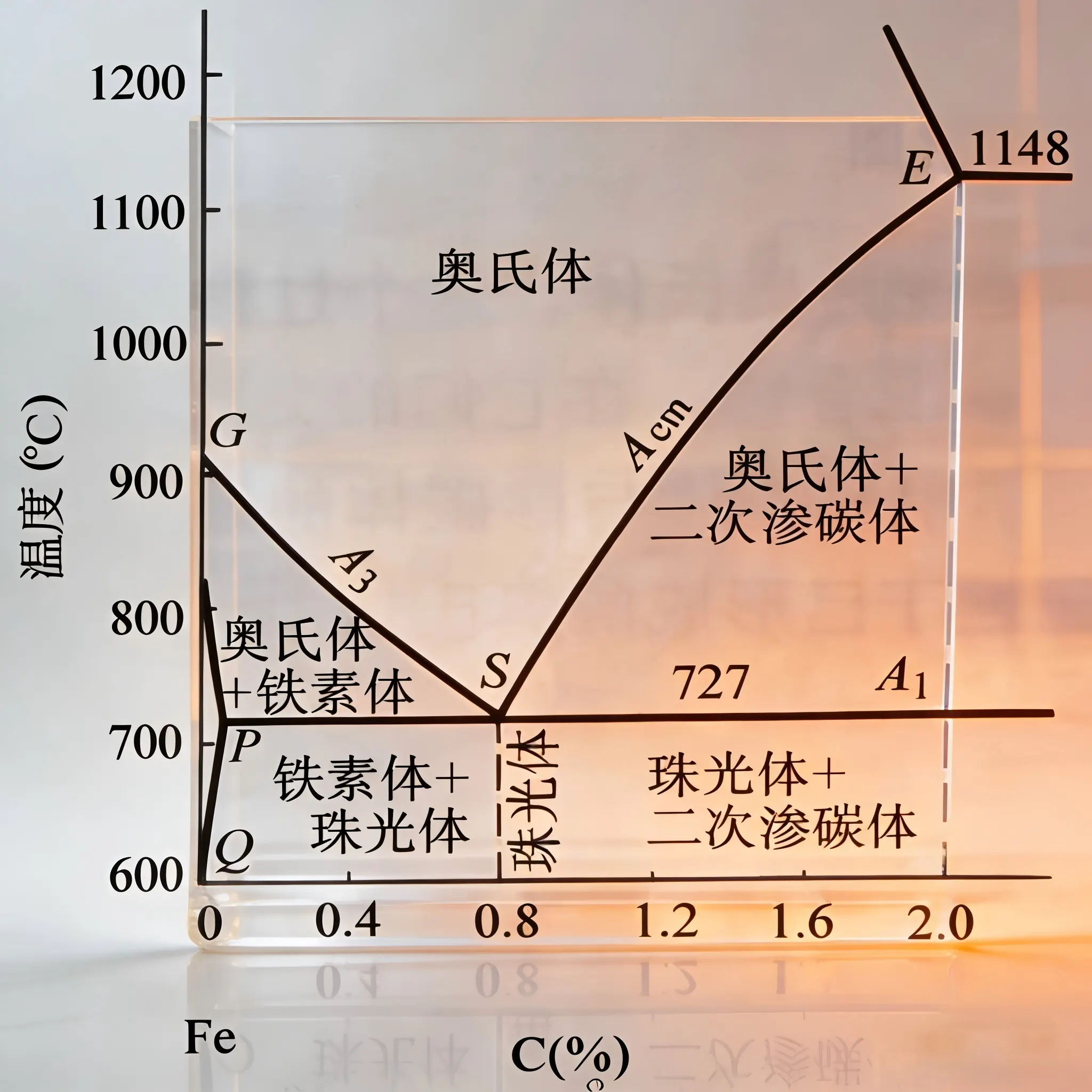
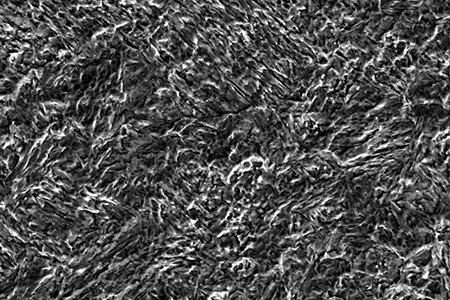
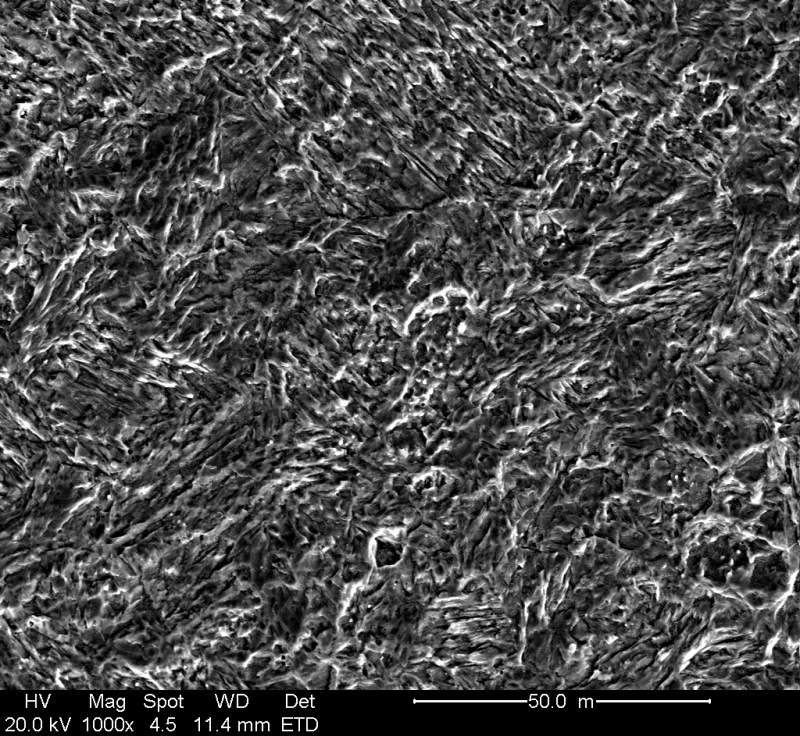
2.2 Microstructural Characteristics
After heat treatment, ZG06Cr13Ni5Mo forms a typical lath martensite structure, which is the microstructural basis for its excellent mechanical properties.
| Structure Type | Content Range | Characteristics and Functions |
|---|---|---|
| Lath Martensite | 80~90% | Matrix structure, provides high strength and hardness; high dislocation density exists between laths |
| Retained Austenite | 8~12% | Distributed between martensite laths; improves toughness and plasticity through TRIP effect |
| Carbides | Small amount | Dispersion distribution, further strengthens matrix, improves wear resistance |
2.3 Physical Properties
ZG06Cr13Ni5Mo has good physical properties, meeting the basic requirements of engineering applications.
| Property Index | Value | Testing Conditions |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 7.79 kg/dm³ | Room temperature |
| Specific Heat Capacity | 0.47 J/(g·K) | Room temperature |
| Thermal Conductivity | 16.3 W/(m·K) | Room temperature |
| Coefficient of Linear Expansion | 10.7×10⁻⁶/K | 20~100°C |
| Elastic Modulus | 200 GPa | Room temperature |
3. Mechanical Properties Analysis
3.1 Room Temperature Mechanical Properties
ZG06Cr13Ni5Mo exhibits excellent room temperature mechanical properties, achieving a good balance between strength and toughness.
| Property Index | Value Range | Testing Standard |
|---|---|---|
| Tensile Strength (Rm) | 1050~1250 MPa | GB/T 228.1 |
| Yield Strength (Rp0.2) | ≥850 MPa | GB/T 228.1 |
| Elongation (A) | ≥12% | GB/T 228.1 |
| Reduction of Area (Z) | ≥45% | GB/T 228.1 |
| Brinell Hardness (HBW) | 221~286 | GB/T 231.1 |
3.2 Low Temperature Impact Properties
The material retains good toughness at low temperatures, which is crucial for applications in cold regions and low-temperature working conditions.
| Testing Temperature | Impact Absorption Energy (KV₂) | Testing Standard |
|---|---|---|
| 0°C | ≥50 J | GB/T 229 |
| -20°C | ≥40 J | GB/T 229 |
| -40°C | ≥35 J | GB/T 229 |
3.3 Fatigue Properties
ZG06Cr13Ni5Mo has good fatigue properties and can withstand long-term alternating load applications.
| Property Index | Value | Testing Conditions |
|---|---|---|
| Fatigue Limit (σ-1) | 550 MPa | 10⁷ cycles |
| Fatigue Strength Coefficient | 1200 MPa | – |
| Fatigue Ductility Coefficient | 0.08 | – |
3.4 Performance Advantage Analysis
Compared with traditional martensitic stainless steels, ZG06Cr13Ni5Mo has significant advantages in multiple performance indicators:
| Performance Index | ZG06Cr13Ni5Mo | Traditional 13Cr Stainless Steel | Improvement |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tensile Strength | 1050~1250 MPa | 800~950 MPa | 25~30% |
| -40°C Impact Energy | ≥35 J | ≥20 J | 75% |
| Pitting Potential | +320 mV(SCE) | +200 mV(SCE) | 60% |
| Corrosion Rate | 0.012 mm/a | 0.025 mm/a | 52% |
4. Manufacturing Process Technology
4.1 Smelting Process
The smelting of ZG06Cr13Ni5Mo adopts an advanced dual refining process to ensure high purity and composition uniformity of the material.
| Process Stage | Technical Parameters | Control Objectives |
|---|---|---|
| Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) | Vacuum degree ≤1×10⁻³Pa | Degassing, precise composition control |
| Argon Oxygen Decarburization (AOD) | Carbon content ≤0.06% | Deep decarburization, composition adjustment |
| Refining Time | 60~90 minutes | Impurity removal, composition homogenization |
| Gas Content | H≤3 ppm, O≤80 ppm, N≤180 ppm | Improve purity |

4.2 Casting Process
The investment casting process is adopted, enabling the production of high-precision castings with complex shapes.
| Process Parameters | Technical Requirements | Quality Standards |
|---|---|---|
| Binder System | Silica sol-ethyl silicate composite | – |
| Shell Face Layer | 200 mesh zircon powder + 325 mesh fused silica | Surface roughness Ra≤6.3μm |
| Pouring System | Bottom pouring stepped runner + spherical riser | Density ASTM E505 Grade 1 |
| Pouring Temperature | 1580~1620°C | Good fluidity |
| Cooling Rate | 5~10°C/min | Avoid cracks |
4.3 Heat Treatment Process
The optimized heat treatment process is a key step to achieve excellent performance.
| Process Stage | Technical Parameters | Microstructural Transformation |
|---|---|---|
| Quenching | 1030°C×30min, oil quenching | Austenite → Martensite |
| First Tempering | 580°C×4h, air cooling | Martensite decomposition, carbide precipitation |
| Second Tempering | 580°C×2h, furnace cooling | Retained austenite stabilization |
| Heating Rate | ≤100°C/h | Avoid thermal stress |
| Cooling Rate | Furnace cooling ≤50°C/h | Structure stabilization |
4.4 Surface Treatment Process
The low-pressure vacuum plasma nitriding technology is adopted to further improve surface hardness and wear resistance.
| Process Parameters | Technical Indicators | Treatment Effects |
|---|---|---|
| Treatment Temperature | 520°C | Avoid matrix softening |
| Nitrogen Partial Pressure | 3 kPa | Compound layer formation |
| Treatment Time | 8 hours | Nitrided layer thickness control |
| Compound Layer Thickness | 20~30μm | ε-Fe₂₋₃N phase |
| Surface Hardness | 1100 HV0.05 | 76% improvement |
6. Corrosion Resistance and Surface Properties
5.1 Corrosion Resistance
ZG06Cr13Ni5Mo has excellent corrosion resistance, particularly outstanding performance in chloride-containing environments.
| Testing Item | Technical Indicators | Testing Standard |
|---|---|---|
| Pitting Potential | +320 mV(SCE) | GB/T 17899 |
| Corrosion Rate | 0.012 mm/a | GB/T 10124 |
| Intergranular Corrosion | No corrosion | GB/T 4334 |
| Stress Corrosion | Crack growth rate <10⁻⁸mm/s | GB/T 15970 |
5.2 Wear Resistance
After surface treatment, the wear resistance of the material is significantly improved.
| Testing Conditions | Wear Loss | Performance Comparison |
|---|---|---|
| Dry Friction | 76% reduction | After nitriding treatment |
| Silt-containing Water Erosion | 65% reduction | After nitriding treatment |
| Sliding Wear | Wear rate 0.5×10⁻⁶mm³/(N·m) | – |
5.3 Surface Property Optimization
Through various surface treatment technologies, the surface properties of the material can be further optimized:
| Treatment Technology | Surface Hardness | Nitrided Layer Thickness | Applicable Working Conditions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Plasma Nitriding | 1100 HV0.05 | 20~30μm | Wear, corrosion environments |
| Laser Surface Quenching | 850 HV0.05 | 0.5~1.0mm | Local strengthening |
| Electroless Nickel Plating | 500 HV0.05 | 10~20μm | Corrosion protection, decoration |
5. Professional Manufacturing Capability
5.1 Leesh Holdings – Sand Casting Foundry
Leesh Holdings is a professional sand casting foundry with complete manufacturing capabilities for high-end stainless steel castings such as ZG06Cr13Ni5Mo. The company has advanced melting equipment, precision casting processes, and strict quality control systems, providing customers with one-stop services from material selection, process design to finished product delivery.
Technical advantages of Leesh Holdings include:
- Advanced Melting Equipment: Equipped with vacuum induction melting furnace and argon oxygen decarburization refining furnace to ensure material purity
- Sand Casting Process: Adopting advanced sand casting technology , with surface roughness up to Ra 6.3–25 μm
- Complete Heat Treatment Line: Computer-controlled multi-stage heat treatment furnace to ensure performance stability
- Strict Quality Testing: Equipped with direct reading spectrometer, universal testing machine, non-destructive testing equipment, etc.
- Rich Engineering Experience: Successful cases in hydro turbines, offshore engineering, nuclear power equipment and other fields
For more information about ZG06Cr13Ni5Mo casting manufacturing capabilities or to seek cooperation, please contact:
6. Engineering Application Cases
6.1 Hydro Turbine Runner Applications
ZG06Cr13Ni5Mo is an ideal material for hydro turbine runners, capable of withstanding the impact and abrasion of high-speed water flow.
| Application Parameters | Technical Indicators | Operating Effects |
|---|---|---|
| Runner Diameter | 4.3 meters | Maximum efficiency 94.5% |
| Design Head | 678 meters | Suitable for high head conditions |
| Peak Shaving Response Time | ≤85 seconds | Rapid response capability |
| Design Life | 50 years | Long-term stable operation |
| Vibration Control | 25%-45% of rated speed | Stable operation |

6.2 Offshore Engineering Applications
In marine environments, ZG06Cr13Ni5Mo demonstrates excellent seawater corrosion resistance.
| Application Components | Technical Parameters | Service Performance |
|---|---|---|
| Grade R5 Steel Anchor Chain | Single link load 1250kN | 25% improvement over Grade R4 |
| South China Sea Deepwater Oilfield | H₂S-containing acidic environment | No significant corrosion after 3 years service |
| Stress Corrosion Crack Growth Rate | <10⁻⁸mm/s | Far below safety threshold |
| Surface Condition | Complete passivation film | Good corrosion protection |
6.3 Nuclear Power Equipment Applications
In the nuclear power field, ZG06Cr13Ni5Mo is used to manufacture key safety components.
| Application Components | Technical Requirements | Performance |
|---|---|---|
| Nuclear Pump Bodies | Seismic Class 1 | Meets safety requirements |
| Control Rod Drive Mechanisms | Fatigue life 10⁶ cycles | Long-term reliable operation |
| Reactor Cooling Systems | 350°C high temperature and pressure | Stable performance |
| Radiation Shielding Performance | Good neutron absorption | Safety protection |
6.4 Other Industrial Applications
ZG06Cr13Ni5Mo is also widely used in chemical, petroleum, food processing and other fields.
| Application Field | Specific Components | Technical Requirements |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Industry | Reactores, heat exchangers | Corrosion resistance, high temperature resistance |
| Petroleum Machinery | Valves, pipelines | Wear resistance, erosion resistance |
| Food Processing | Canning equipment, packaging machinery | Hygienic grade, corrosion resistance |
| Pharmaceutical Equipment | Reactors, pipeline systems | Clean grade, corrosion resistance |
8. Standards and Quality Control
7.1 Relevant Standards
The production and inspection of ZG06Cr13Ni5Mo comply with multiple national and industry standards.
| Standard Number | Standard Name | Applicable Scope |
|---|---|---|
| GB/T 6967 | Medium and High Strength Stainless Steel Castings for Engineering Structures | Chemical composition, mechanical properties |
| JB/T 6405 | Large Stainless Steel Castings | Dimension tolerances, surface quality |
| GB/T 222 | Permissible Deviations for Chemical Composition of Steel Products | Composition control |
| GB/T 228.1 | Metallic Materials – Tensile Testing | Mechanical property testing |
| GB/T 229 | Metallic Materials – Charpy Pendulum Impact Test | Impact property testing |
| GB/T 17899 | Test Method for Pitting Potential of Stainless Steels | Corrosion resistance testing |
7.2 Quality Control System
A comprehensive quality control system is established to ensure stable and reliable product quality.
| Control Link | Control Items | Control Standards |
|---|---|---|
| Raw Materials | High purity iron, alloying elements | C≤20ppm, P≤3ppm, S≤3ppm |
| Smelting Process | Temperature, time, composition | Real-time monitoring, automatic control |
| Casting Process | Shell quality, pouring parameters | Surface roughness Ra≤6.3μm |
| Heat Treatment | Temperature, time, cooling rate | Computer precise control |
| Nondestructive Testing | UT, MT, PT | Internal quality, surface quality |
| Performance Testing | Tensile, impact, hardness | 100% inspection |
7.3 Testing Technology
Advanced testing technologies are adopted to ensure product quality meets requirements.
| Testing Item | Testing Method | Testing Accuracy |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Composition | Direct reading spectrometer | 0.001% |
| Gas Content | Oxygen-nitrogen-hydrogen analyzer | 1ppm |
| Internal Defects | Ultrasonic Testing (UT) | φ0.8mm |
| Surface Defects | Magnetic Particle Testing (MT), Penetrant Testing (PT) | Microcracks |
| Mechanical Properties | Electronic universal testing machine | 0.5 grade |
| Microstructure | Metallographic microscope, scanning electron microscope | 0.1μm |
9. Conclusions and Implications
8.1 Main Conclusions
Through comprehensive analysis of ZG06Cr13Ni5Mo material, the following main conclusions can be drawn:
- Reasonable Composition Design: By reducing carbon content and optimizing the ratio of alloying elements such as nickel and molybdenum, the perfect combination of high strength with good toughness and corrosion resistance is achieved.
- Excellent Performance: Tensile strength reaches 1050-1250MPa, -40°C impact energy ≥35J, pitting potential +320mV(SCE), all performance indicators are superior to traditional martensitic stainless steels.
- Mature Technology: Adopting vacuum induction melting + argon oxygen decarburization dual refining process, investment casting process, and optimized heat treatment process enables stable production of high-quality castings.
- Wide Applications: Successfully applied in multiple fields such as hydro turbines, offshore engineering, and nuclear power equipment, demonstrating broad application prospects.
- Comprehensive Standards: A comprehensive standard specification system and quality control system have been established to ensure stable and reliable product quality.
8.2 Technical Implications
The research and application of ZG06Cr13Ni5Mo provide important implications for China’s high-end material development:
- Material Design Innovation: Through precise composition design and process optimization, the performance limitations of traditional materials can be broken, developing new materials with excellent comprehensive properties.
- Process Technology Progress: Advanced smelting, casting and heat treatment processes are key to achieving high material performance, requiring continuous promotion of process technology innovation and progress.
- Standard System Construction: A comprehensive standard specification system is an important foundation for ensuring product quality and promoting industrial development, requiring strengthening of standard formulation and implementation.
- Application Field Expansion: The application of high-performance materials can drive technological progress of relevant equipment, requiring strengthening of collaborative innovation between materials and equipment.
8.3 Development Prospects
As China’s equipment manufacturing industry develops towards high-end and intelligent directions, the demand for high-performance materials will continue to grow. As a high-end stainless steel material with excellent comprehensive properties, ZG06Cr13Ni5Mo has broad development prospects:
- Market Demand Growth: Development in energy, marine, nuclear power and other fields will drive demand growth for high-strength corrosion-resistant stainless steel materials.
- Technology Upgrade Space: Through further optimization of composition design and process technology, a new generation of materials with more excellent performance can be developed.
- Application Field Expansion: With the improvement of material performance and cost reduction, application fields will continue to expand, further expanding market space.
- Industrial Upgrade Promotion: The development of high-end materials will drive technological upgrading and product quality improvement in relevant industries, promoting China’s manufacturing industry to move towards the high end of the value chain.
References
Appendix A Tensile Test Report
Sample Number: ZG2025-001
Testing Standard: GB/T 228.1-2010
Test Results:
– Tensile Strength (Rm): 1180 MPa
– Yield Strength (Rp0.2): 920 MPa
– Elongation (A): 14.5%
– Reduction of Area (Z): 48%
Appendix B Impact Test Report
Sample Number: ZG2025-002
Testing Standard: GB/T 229-2020
Test Results:
– 0°C Impact Energy: 58 J
– -20°C Impact Energy: 45 J
– -40°C Impact Energy: 38 J
Appendix C Corrosion Resistance Test Report
Sample Number: ZG2025-003
Testing Standard: GB/T 17899-1999
Test Results:
– Pitting Potential: +335 mV(SCE)
– Corrosion Rate: 0.011 mm/a
– Polarization Resistance: 5.2×10⁴ Ω·cm²
Prepared by: Material Engineering Technology Center
Report Date: December 2025
Version: V1.0